Beyond certification: Using ISO 9001 for QMS development
June 6, 2025
Building a quality management system (QMS) from the ground up can feel overwhelming—where do you begin, and how do you make sure it actually works? Many organizations look to ISO 9001 for answers. It’s the world’s most widely adopted quality standard, used across industries and borders to promote consistency and trust.
But can this globally recognized standard truly serve as a foundational guide for developing your QMS—not just for auditing it after the fact?
In this article, we’ll walk you through exactly how ISO 9001 supports QMS development from day one. You’ll learn how its structure, principles, and clauses provide a practical, flexible roadmap for building a system that fits your organization, meets requirements, manages risk, and drives continuous improvement.
What is a QMS?
A Quality Management System, or QMS, is essentially your organization's structured blueprint for ensuring consistent quality. It maps out how work gets done—through defined processes, responsibilities, and controls—to ensure results are consistent, not left to chance. A good QMS helps you meet customer and regulatory requirements without guesswork, reduce risk by design, and improve steadily over time. More than documentation, it’s a disciplined way of thinking. One that lets you build trust—by doing things right, again and again.
What is ISO 9001 and its seven principles?
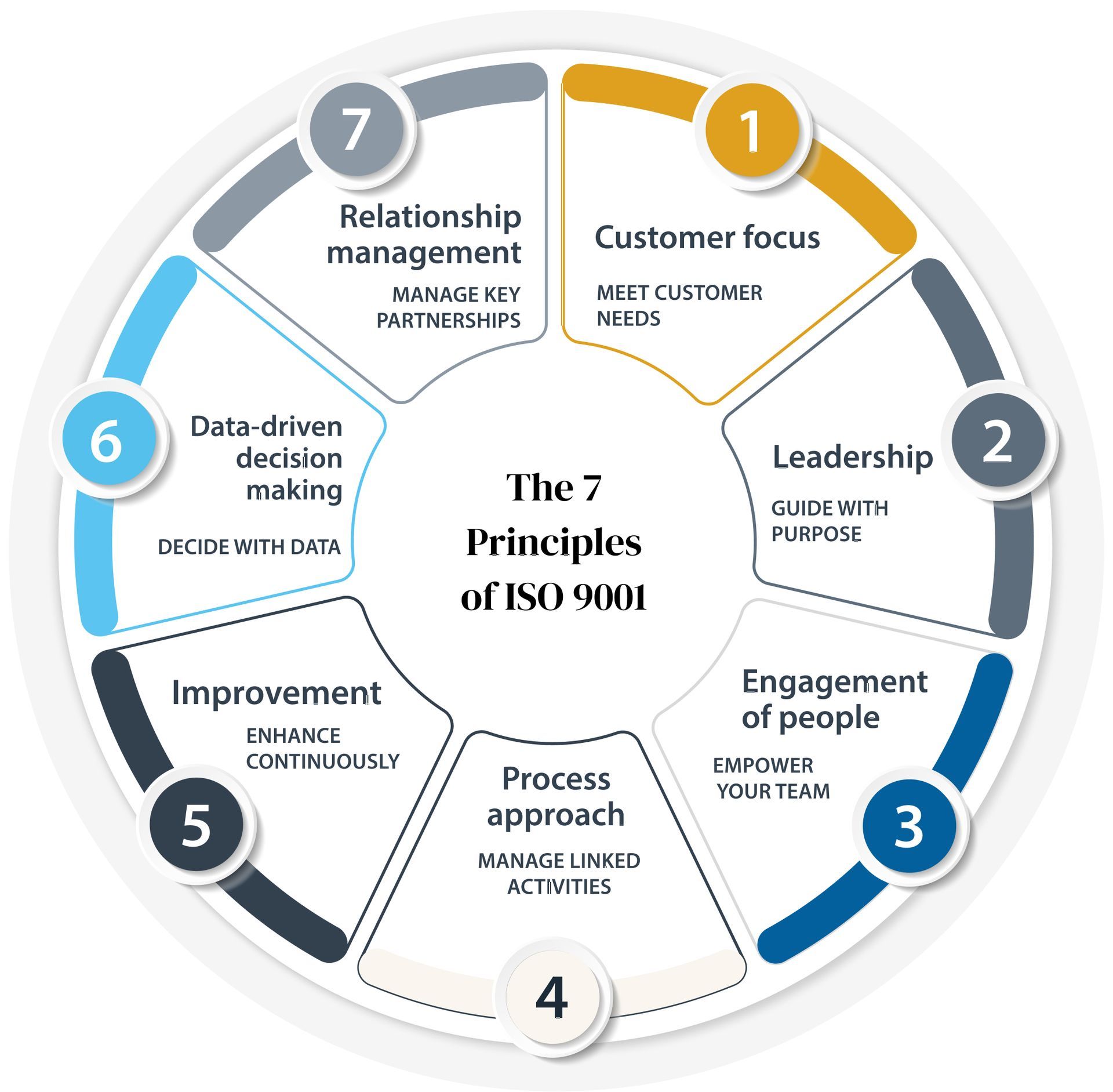
While your QMS is the internal blueprint for how your organization operates, ISO 9001 provides the globally recognized foundation for building it. The standard doesn’t tell you how to run your business—it defines what your system must achieve: consistent quality, regulatory compliance, risk control, and ongoing improvement. It’s a guide for establishing, maintaining, and strengthening your QMS over time. Grounded in seven core principles, ISO 9001 helps ensure your organization stays focused on what matters most—meeting customer needs, reliably and repeatedly.
The ISO 9001 requirements help structure your QMS around measurable objectives, defined responsibilities, and a built-in feedback loop for improvement. Figure 1 below shows the 7 principles of ISO 9001.
How ISO 9001 Supports QMS Development
ISO 9001 offers a structured yet flexible foundation for developing a quality management system tailored to your organization’s purpose, size, and complexity. Its strength lies in three core practices: clear process documentation, which ensures consistency and transparency across operations; risk-based thinking, which enables you to anticipate and address issues before they affect quality or customer satisfaction; and a disciplined commitment to continual improvement, which drives your organization to refine processes and raise performance over time. Figure 2 below shows how ISO 9001 clauses 4-10 guide QMS development.
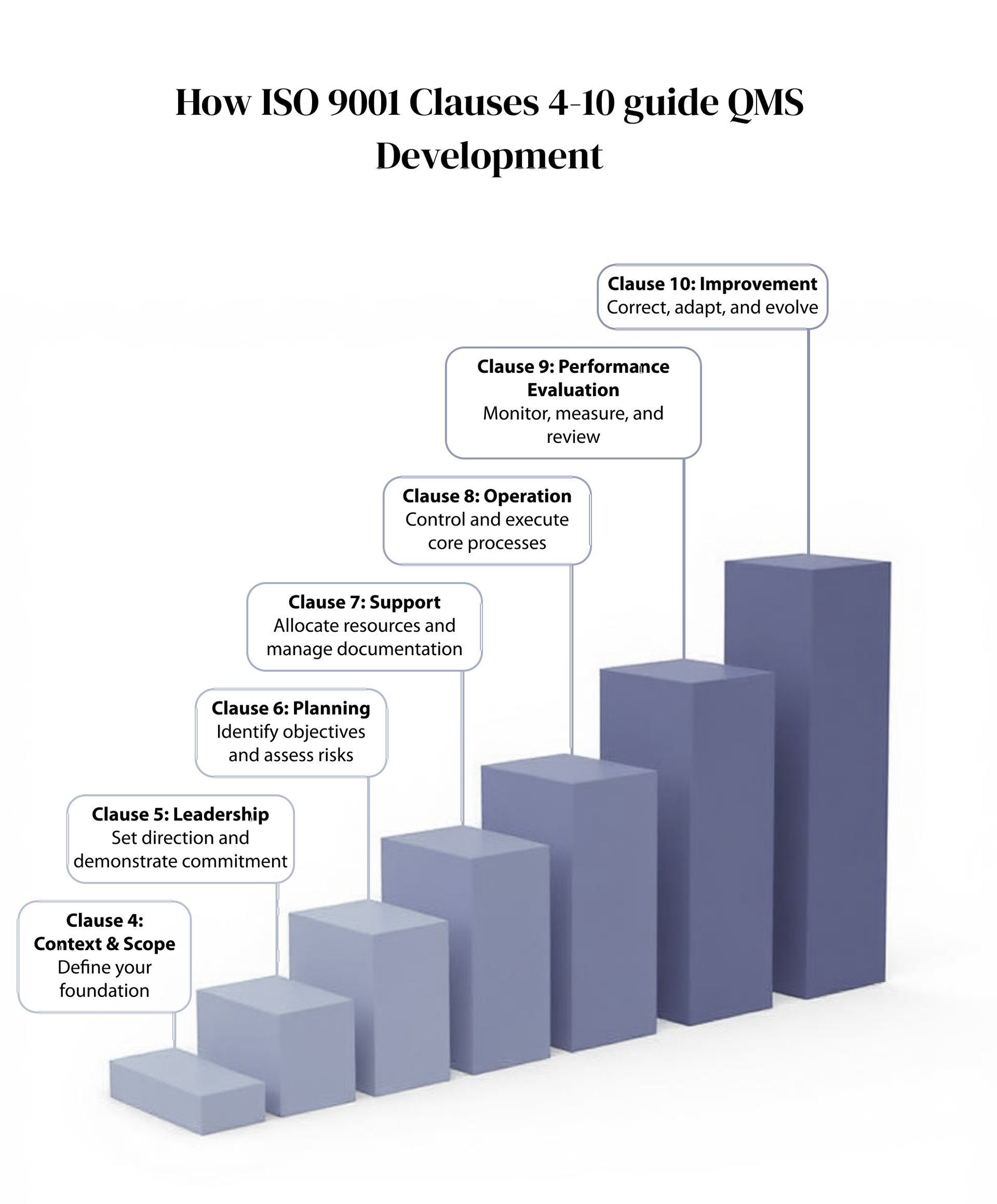
These clauses follow a natural order, guiding you through every stage of QMS development—from strategic alignment to day-to-day execution and long-term refinement.
Strategic Advantages and Ideal Scenarios for Using ISO 9001 in Development
Using ISO 9001 from the beginning sets the tone for how quality is understood and practiced across teams. It brings clarity and consistency to your processes, making it easier to document how things are done and why. This structure eliminates ambiguity and supports repeatable performance.
Risk-based thinking is embedded from the start, guiding you to identify and address potential issues proactively, rather than reacting to problems. At the same time, ISO 9001 encourages a customer-first mindset, ensuring your processes are aligned with what matters most to those you serve. The principle of continuous improvement keeps your system from becoming static—it pushes your organization to keep learning, adapting, and improving.
Even if certification isn’t your immediate goal, using ISO 9001 lays the groundwork, making future certification faster, cheaper, and smoother. It also promotes strong organizational alignment, breaking down silos by directing various departments towards shared quality objectives.
This approach is especially valuable for organizations at key transition points—startups building their systems from the ground up, established businesses formalizing quality practices, or companies preparing for growth, industry-specific demands, or international expansion. In each case, ISO 9001 provides a clear, proven framework that transforms quality from a reactive function into a strategic advantage.
Addressing Common Misconceptions and Challenges
Many organizations hesitate to adopt ISO 9001 because of persistent myths. One of the most common is that it’s overly bureaucratic or focused on paperwork. In reality, ISO 9001 is built for flexibility—it emphasizes effective processes and outcomes, not bloated documentation.
Another misconception is that it’s only suitable for large enterprises. In fact, the standard is scalable and has been successfully implemented by small businesses, nonprofits, and startups across industries. Whether you're considering ISO 9001 for small business use or enterprise-level implementation, the framework adapts to your size, structure, and needs.
Some view it as a one-time project for certification, overlooking that QMS development is an ongoing journey of continuous improvement.
Challenges do arise—particularly limited internal expertise or resistance to change. These can be addressed through training, leadership support, and phased implementation.
It’s also important to remember what ISO 9001 doesn’t provide: prescriptive tools, off-the-shelf workflows, or sector-specific procedures. These must be developed internally to reflect your unique context—and that’s where the real strength of your QMS lies.
Practical Steps for Using ISO 9001 in your QMS Development
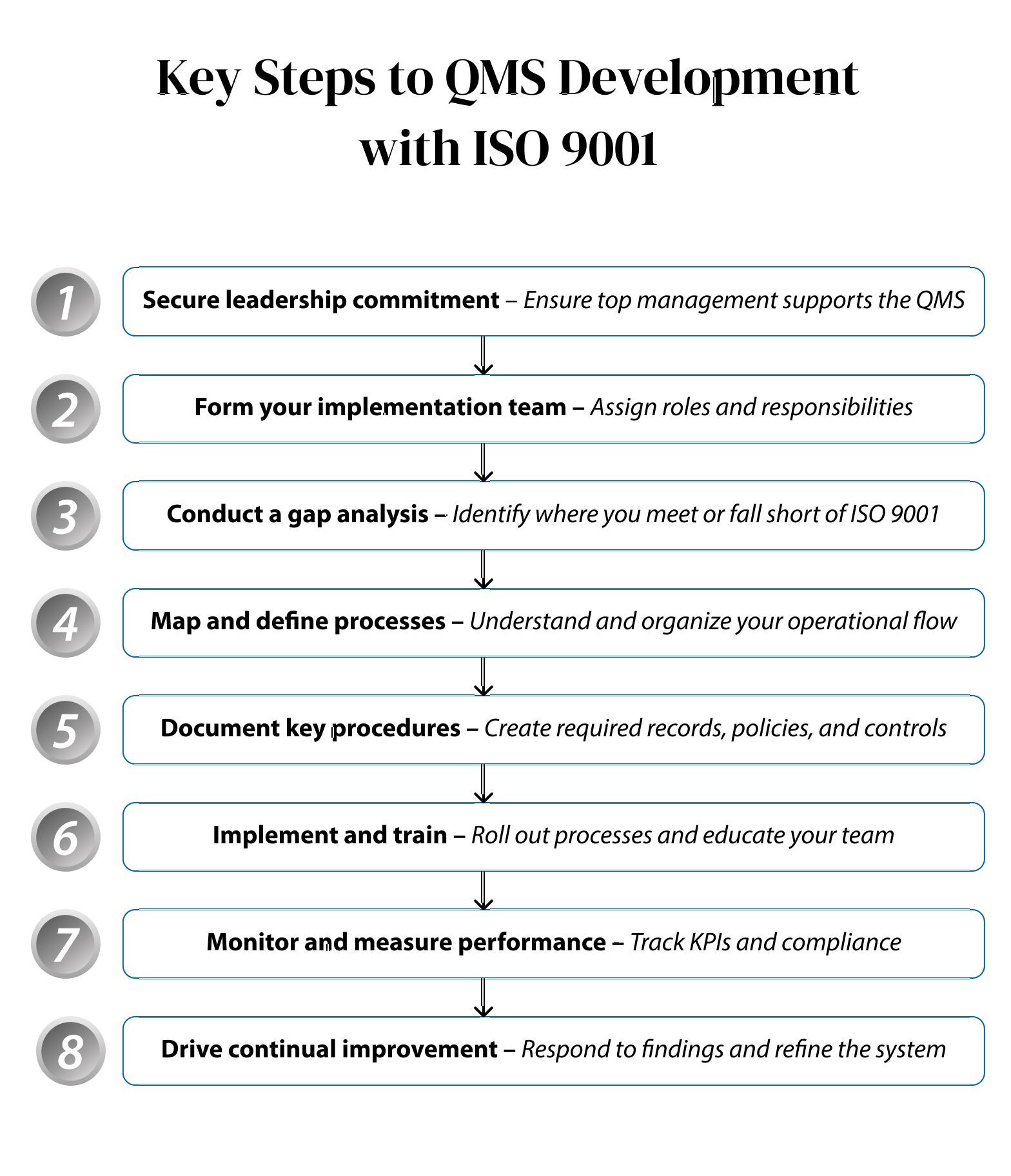
Turning ISO 9001 into a working QMS starts with intent. The standard offers structure, but it’s your organization that gives it shape.
Below see Figure 3--a practical sequence of steps grounded in the standard’s structure. Each one moves you closer to a system that not only meets requirements but helps your organization run more smoothly, respond to change, and deliver consistent value.
Complementary Tools and Standards for Enhanced Quality
While ISO 9001 provides the framework, additional tools and standards can strengthen how your QMS operates day to day. For auditing, ISO 19011 offers practical guidance on planning and conducting internal audits. In the automotive sector, IATF 16949 builds on ISO 9001 with industry-specific requirements.
For process optimization, Lean and Six Sigma methodologies help eliminate waste and reduce variation. These tools reinforce QMS best practices by encouraging consistency, analysis, and evidence-based improvement.
Digital QMS software platforms can streamline documentation, version control, and corrective action tracking—making the system more usable and less burdensome.
Depending on your sector, other standards or regulatory frameworks may apply. The key is to use ISO 9001 as your foundation, then layer in tools that support your goals, industry context, and operational needs.
In Conclusion
ISO 9001 is not just suitable for QMS development—it’s one of the most valuable frameworks you can use. It brings structure, clarity, and accountability to your operations while staying flexible enough to fit any organization. With its focus on risk management, customer satisfaction, and continual improvement, it helps you shift from reactive problem-solving to proactive, reliable performance.
Whether you're starting from scratch or refining an existing system, ISO 9001 offers a clear path toward stronger alignment, better outcomes, and long-term growth. It won’t prescribe your methods—but it will help you build a system that works, evolves, and earns trust.
ISO 9001 isn’t just for passing audits—it’s for building systems that actually work.
Ready to build a quality foundation that lasts?
Start by gaining the skills and credentials that matter. Explore our professional certification courses:
ISO 9001 Lead Implementer
– Master the design and rollout of a QMS.
ISO 9001 Lead Auditor
– Learn how to assess and improve quality systems.
Take the next step toward operational excellence—your journey starts here.
Share this article