Choosing Between ISO 9001 and ISO/IEC 27001? Here’s Why You Might Need Both
June 3, 2025
Today it's more important than ever to ensure the safety and security of your business. As businesses expand, global standards offer a way to achieve sustainable growth. Among the most popular of these standards are ISO 9001 and ISO/IEC 27001.
Both standards contain similarities that aim to improve organizational management systems; however, they both serve distinct purposes. One focuses on quality management, the other on information security. In many cases, choosing one over the other is not the best answer. Understanding how these standards complement each other and how to apply both to maintain security will yield a much greater benefit to you and your business.
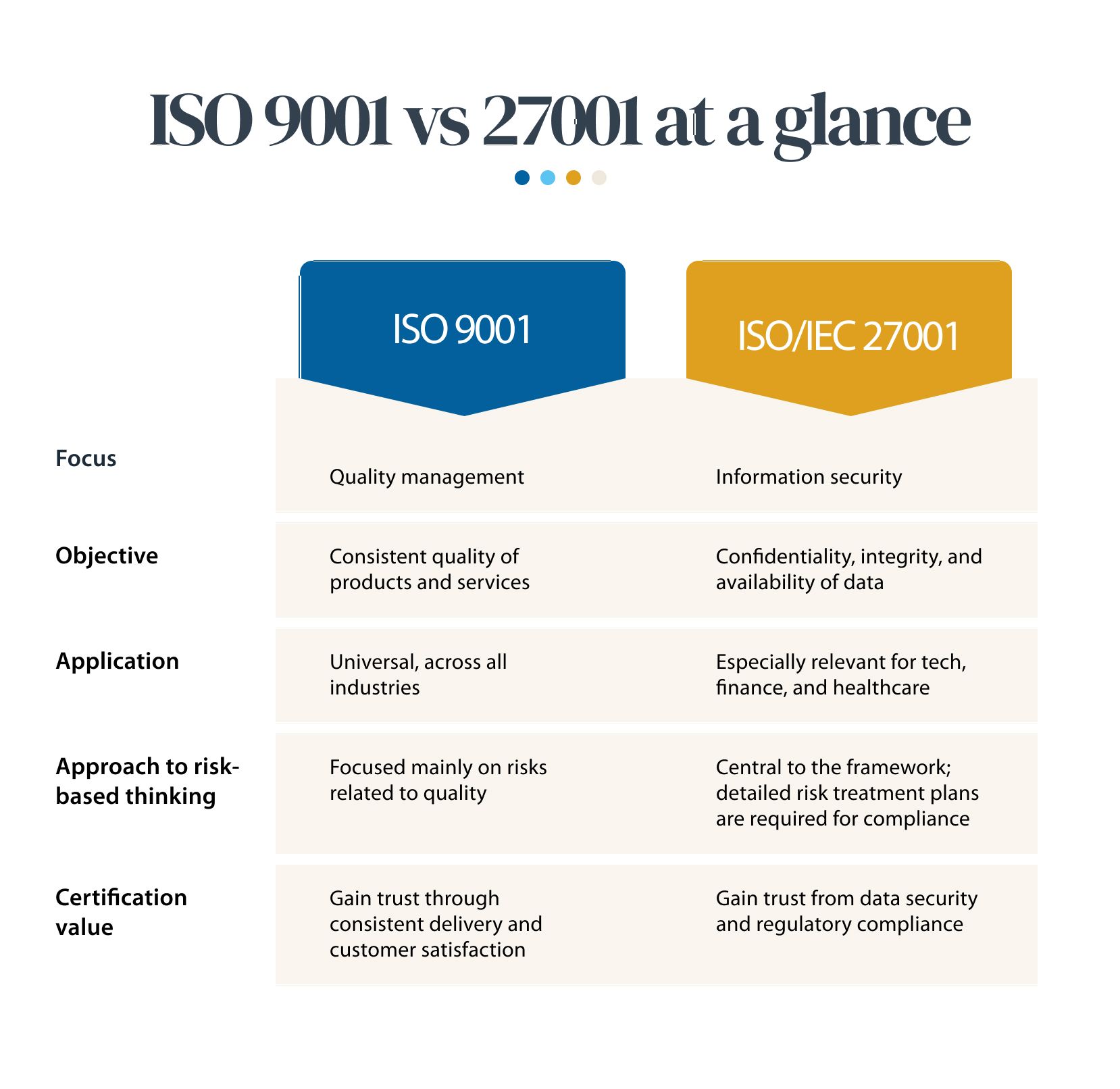
ISO 9001 – Quality Management Systems
- Customer satisfaction (e.g. building and maintaining various customer support channels or sending out customer satisfaction surveys).
- Process optimization (e.g. automating workflows to minimize delays and waste).
- Leadership alignment (e.g. communicating goals across departments).
- Evidence-based decision making (e.g. adjusting operations based on customer data and feedback).
- Risk-based thinking (e.g. conducting risk analyses and implementing respective safeguards).
ISO/IEC 27001 – Information Security Management
In contrast, ISO/IEC 27001 is the world’s most recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS), defining what requirements an ISMS must meet. It provides risk-based guidance on identifying and mitigating information security risks, both from inside and outside of the organization.
While ISO 9001 focuses on providing quality products and services, ISO/IEC 27001 focuses on maintaining and protecting what makes that quality possible. It looks to safeguard the data, infrastructure and internal systems of day-to-day business operations.
The standard focuses on:
- Asset management (e.g. building and maintaining an inventory of all company software or accounts).
- Access control (e.g. Using user permissions to restrict access of data to specified personnel).
- Risk assessment and treatment (e.g. assessing the current ISMS and identifying vulnerabilities).
- Security incident response (e.g. setting up a specific response process for detecting, reporting, and responding to cybersecurity events).
- Compliance with legal, contractual, and regulatory obligations (e.g. ensuring that the company’s ISMS complies with any relevant regulatory requirements, such as the GDPR).
ISO/IEC 27001 helps businesses protect their intellectual property, as well as client and partner data. It promotes a holistic approach to security; overseeing people, internal policies, and technology. Any ISMS implemented under the guidance of ISO/IEC 27001 is a reliable tool for cyber resilience, risk management and operational excellence.
Let’s look at an example of ISO/IEC 27001 in action, just as we did for ISO 9001 in the last section. Imagine a financial services company that provides customers with loans. To properly analyze loan applications, this company would need to handle sensitive customer information such as income statements and identification documents. To comply with ISO/IEC 27001 and protect its customer data, the company has implemented an ISMS.
How does the company’s ISMS work? First, the company uses data encryption and user permissions to ensure that only authorized personnel can view or manage a customer’s data. Second, the company enforces regular cybersecurity awareness training for all employees (e.g. training in safe data storage, password protection, and spotting scam emails). Third, the company’s cybersecurity team monitors unusual activities, logs security events, and manages event response procedures. All these processes are documented and reviewed for potential weaknesses.
Which One is Right for You?
The answer depends on many factors, including the sector your business primarily operates in, the expectations of your clients, and even your own business goals. However, due to business becoming increasingly more digital, many organizations find that adopting both standards provides a comprehensive model of governance that can deliver the right guidance and protection under any circumstances.

One of the biggest advantages of these two standards is how well they integrate with one another. Both share a common framework in terms of terminology and the elements of their respective management systems.
This allows businesses to implement both standards in tandem, which can help to streamline audits and unify documentation and process control systems. It also allows leadership to monitor risk and performance across quality and security through a single, aligned governance model.
Final Thoughts
In the modern world, customer expectations are high, and data threats are becoming more sophisticated every day. The pressure on businesses to meet the quality and security requirements to compete has never been higher.
ISO 9001 and ISO/IEC 27001 offer organizations a way to build trust and reduce risk in day-to-day operations. Building on the foundation these standards set, whether adopting one or both, sets the stage for sustainable growth that will provide a secure future for your business. These standards shape the way your business operates and will quickly become a strategic asset for those looking to compete in the modern world.
If you're considering certification or want to explore how these standards can align with your current governance strategy, we offer training for both ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO 9001, and can equip your team with right tools and knowledge to safeguard the security and reputation of your business.
Share this article





