Building an AI-Ready GRC Program: Integrating ISO/IEC 42001 with Your Existing Risk Management Framework
August 26, 2025
This guide is designed for professionals and compliance teams looking to establish a complete, AI-ready Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) framework by aligning ISO/IEC 42001 with established standards like ISO/IEC 27001, SOC 2, and the NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF 1.0). It explores practical integration strategies to streamline the process, eliminate unnecessary duplication, and build a futureproof AI governance foundation.
The Importance of Integration
| Term/Acronym | Definition |
|---|---|
| AI | Artificial Intelligence – Systems capable of performing tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as decision-making or pattern recognition. |
| AIMS | Artificial Intelligence Management System – A structured framework for governing AI systems, as defined in ISO/IEC 42001. |
| GRC | Governance, Risk, and Compliance – An organization’s strategy for managing risk, ensuring compliance, and enforcing internal governance. |
| ISO/IEC 42001 | The first international standard specifically for managing AI systems. Focuses on risk, oversight, ethics, and continual improvement. |
| ISO/IEC 27001 | A widely adopted standard for managing information security through an Information Security Management System (ISMS). |
| SOC 2 | System and Organization Controls 2 – A voluntary compliance standard based on the Trust Services Criteria, used for evaluating data security and privacy practices. |
| NIST AI RMF 1.0 | The AI Risk Management Framework developed by NIST to guide organizations in identifying and managing AI risks. |
| Risk Register | A centralized list or system that tracks known risks, their severity, likelihood, and mitigation efforts. |
| Control Matrix | A tool used to document and map controls across multiple standards and business units. Useful during audits. |
| Governance Board | A committee responsible for overseeing compliance, ethics, and risk decisions within an organization. |
The Importance of Integration
As artificial intelligence becomes integral to modern business, companies face the challenge of integrating AI risk management into their existing compliance ecosystem. Many already comply with standards like ISO/IEC 27001 for information security, SOC 2 for trust service criteria, or the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Integrating ISO/IEC 42001 and the NIST AI RMF adds a layer of AI-specific governance without starting from scratch.
This strategic alignment reduces audit fatigue, avoids the unnecessary repetition of processes, and ensures your AI systems are secure, transparent, and trustworthy.
Understanding the Core Frameworks: An Overview
ISO/IEC 42001 -- AI Management System
The first international standard focused on AI-specific governance, ISO/IEC 42001 outlines how businesses should establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve an Artificial Intelligence Management System (AIMS). It emphasizes human oversight, transparency, ethical use, data governance, and risk-based controls.
ISO/IEC 27001 -- Information Security Management
A globally adopted standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It provides a structured framework for managing sensitive data, cyber risks, and incident response. Many controls present in ISO/IEC 27001 overlap with those needed for secure and compliant AI system operation.
Soc 2 -- Trust Services Criteria
Developed by the AICPA in 2010, SOC 2 evaluates service providers’ systems based on security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. While not prescriptive, SOC 2 reports show that controls are effectively designed and operate correctly. AI governance intersects with these areas frequently.
NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF 1.0)
Published in 2023, NIST’s AI RMF provides a voluntary framework to help businesses manage risks associated with AI. It’s organized into four core functions: Govern, Map, Measure, and Manage. Its flexible design supports integration with existing GRC practices.
Integration Map: Aligning Frameworks
Here’s how ISO/IEC 42001 aligns and overlaps with the frameworks and standards mentioned above. Understanding this overlap allows you to reduce effort by exploiting processes that already exist.
Key Integration Points
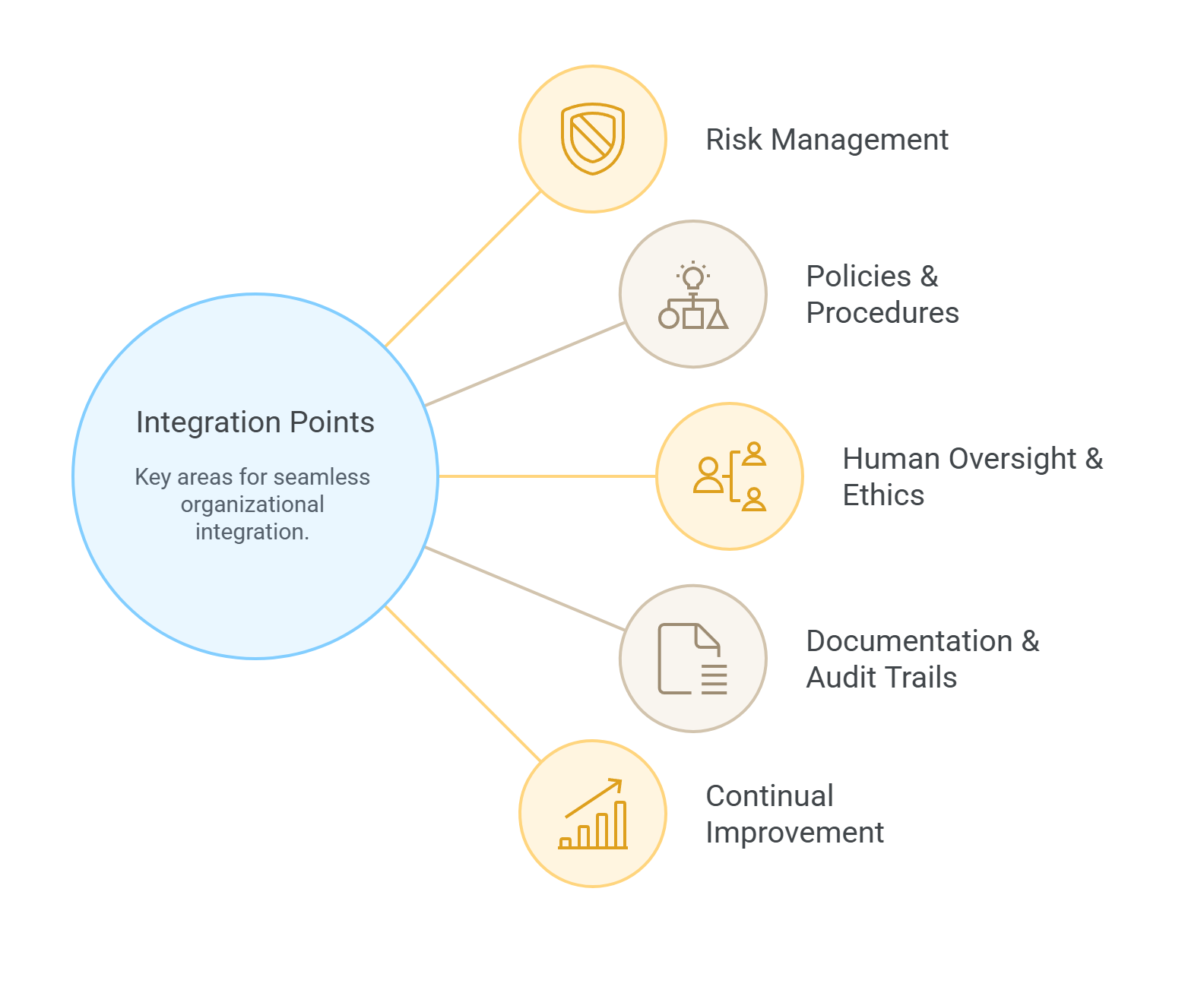
Risk Management:
- ISO 42001, ISO 27001, and NIST AI RMF all emphasize risk-based approaches.
- Use a unified enterprise risk register that includes AI-specific risks alongside cybersecurity and operational risks.
Policies & Procedures:
- Align AI policies (ISO 42001) with security policies (ISO 27001) and privacy statements (SOC 2).
- Use consistent language across frameworks to reduce friction during audits.
Human Oversight & Ethics:
- ISO 42001 and NIST AI RMF both demand meaningful human oversight.
- These can be integrated into existing governance boards or ethics committees already formed under SOC 2 or internal governance programs.
Documentation & Audit Trails:
- Documentation practices under ISO 27001 and SOC 2 provide a strong base for ISO 42001.
- Apply the same version control, access management, and audit trail systems.
Continual Improvement:
- All frameworks emphasize continuous monitoring and improvement.
- Allow existing management review cycles to include AIMS performance and emerging AI risks.
Step-by-Step Integration Roadmap
1. Inventory and Map Existing Controls
Conduct a detailed review of your current compliance landscape. Catalogue all controls already implemented under ISO/IEC 27001, SOC 2, and any existing AI governance efforts. Use this inventory to build a control map that highlights where responsibilities overlap or diverge. Tag controls according to which standard(s) they serve and identify which can be extended to cover AI-specific requirements.
2. Perform a Gap Assessment for ISO/IEC 42001 and NIST AI RMF
Compare your current controls against the clauses and requirements of ISO/IEC 42001 and the functions of the NIST AI RMF. Identify gaps, missing controls, or areas needing adaptation for AI use cases. Look specifically at areas unique to AI (explainability, algorithmic bias, model lifecycle management, and human oversight etc.) to ensure these are addressed appropriately.
3. Develop an Integrated Risk and Control Matrix
Create a consolidated risk and control matrix that integrates requirements across all existing frameworks. This matrix should show how each control maps to the relevant standards and, if applicable, which business unit owns it. Highlight controls that can serve multiple compliance objectives. This tool will be invaluable during audits by helping to demonstrate cohesion and efficiency.
4. Align Governance Structures Across Frameworks
Evaluate whether your current compliance committees or governance boards adequately cover AI governance. If not, update the structure to include cross-functional expertise from legal, risk, data science, and product. Define clear roles and responsibilities and ensure accountability for decisions made about AI systems is well-documented and traceable.
5. Update Policies, Training, and Communication Plans
Review your existing policies and training materials to ensure they cover AI-specific issues. Communicate these changes effectively across departments, emphasizing how AI governance builds on familiar compliance principles. Include awareness training for both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
6. Conduct a Pilot or Internal Audit Against Combined Control
Before moving to formal audits, test your integrated control framework in a single department or business unit. Assess its effectiveness, identify operational challenges, and refine the documentation processes. Conduct an internal audit that evaluates readiness for both ISO/IEC 42001 certification and SOC 2 or ISO 27001 surveillance, incorporating NIST AI RMF checkpoints where appropriate.
7. Engage with Certifying Bodies or External Auditors
Once your integrated program is mature and tested, consult with your certification or audit partners to confirm audit readiness. Present your integrated control matrix, updated policies, and risk assessments. Clarify that while ISO/IEC 42001 is the newest standard, your approach reuses trusted practices from existing certifications, making your AI governance both efficient and credible.
Benefits of an Integrated AI GRC Strategy
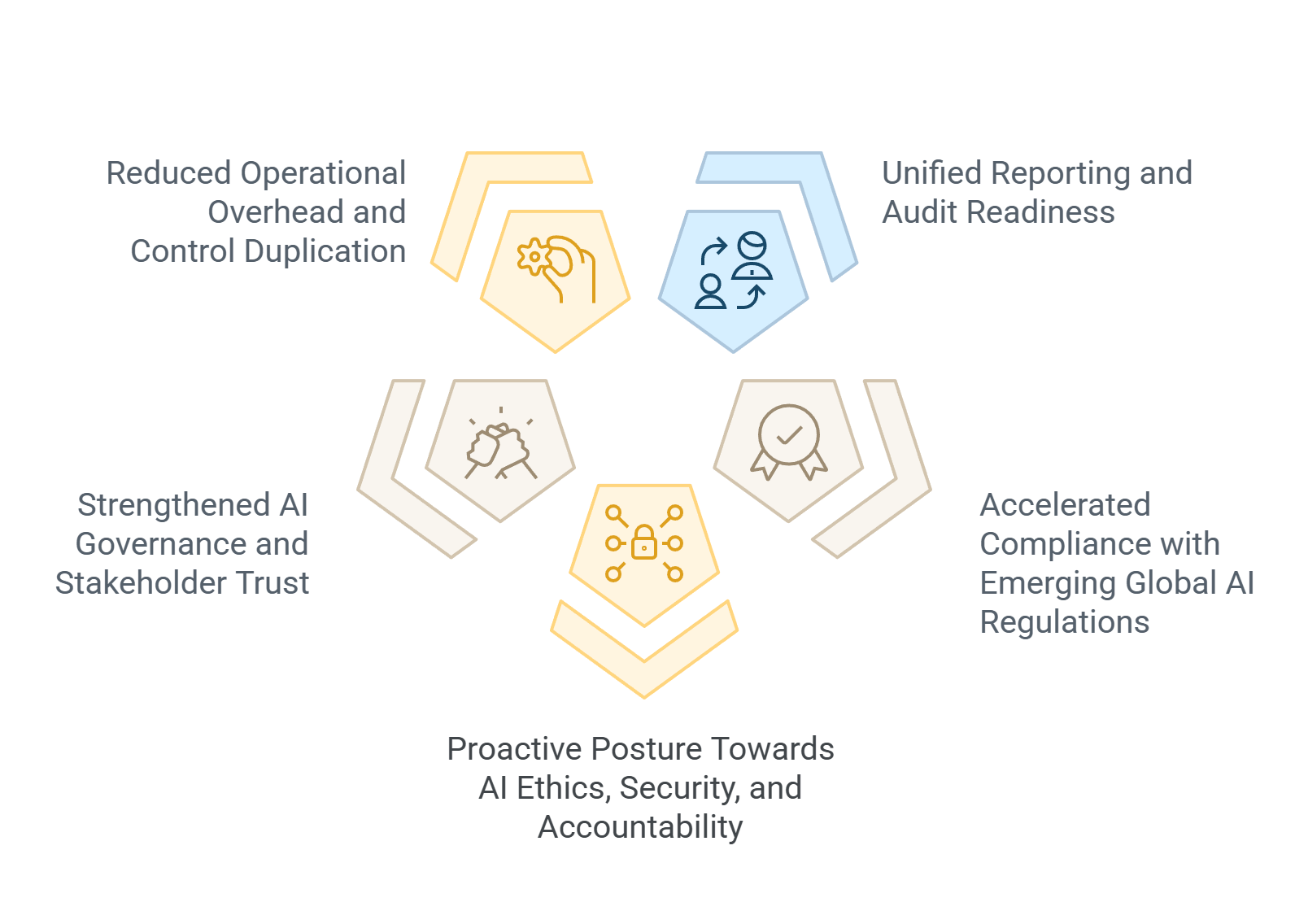
Reduced Operational Overhead and Control Duplication
By aligning and unifying compliance efforts across multiple standards, your organization reduces redundant tasks, removes duplicated controls, and leverages existing systems and documentation. This leads to streamlined audits, shorter implementation cycles, and reduced compliance costs.
Unified Reporting and Audit Readiness
An integrated framework enables centralized dashboards and harmonized audit reports that satisfy multiple standards simultaneously. This simplifies the internal review process and helps external auditors assess compliance faster and with greater confidence.
Strengthened AI Governance and Stakeholder Trust
Demonstrating alignment with leading global standards such as ISO/IEC 42001 and NIST AI RMF reinforces your organization’s commitment to ethical and secure AI practices. This increases internal accountability and enhances trust among partners, customers, regulators, and the broader public.
Accelerated Compliance with Emerging Global AI Regulations
As regulatory bodies worldwide introduce new AI-specific laws (such as the EU AI Act or Canada’s AIDA), your integrated GRC approach positions your business for rapid adaptation. A strong compliance posture allows for quicker localization and implementation of jurisdiction-specific requirements.
A Proactive Posture Toward AI Ethics, Security, and Accountability
Integration encourages a culture of responsible innovation that focuses on looking toward the future. Rather than reacting to risks or regulations, your teams can proactively identify and mitigate emerging threats, ensuring AI systems align with any legal obligations you’re committed to while staying true to your business objectives.
Ready to take the next step in building trusted, AI-ready compliance systems?
Explore our ISO/IEC 42001 Lead Implementer certification course
and equip your team with the skills to integrate AI governance at scale
Share this article





